This educational resource was sponsored by Poise, a brand of Kimberly-Clark. Other Kimberly-Clark brands include Depend and Thinx for All Leaks.
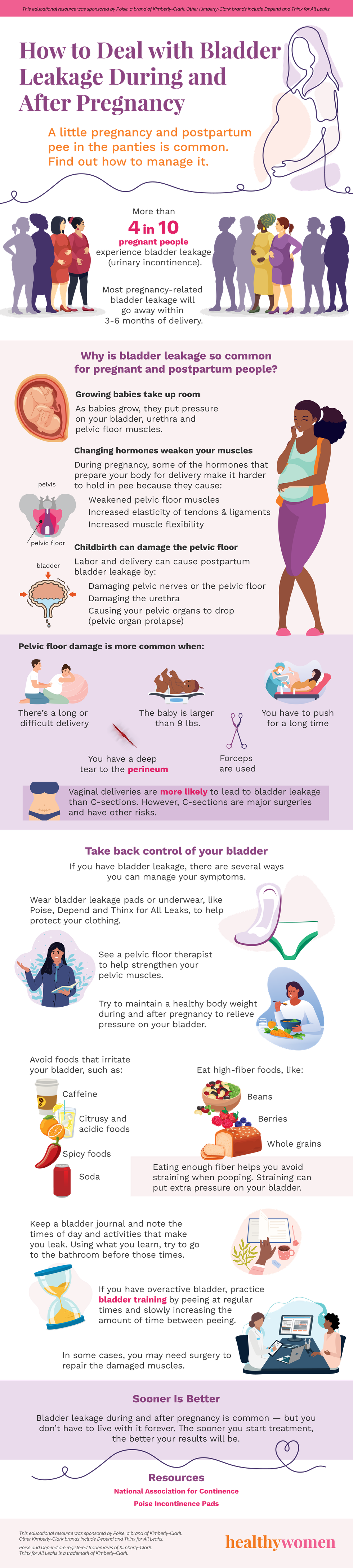
More than 4 in 10 pregnant people experience bladder leakage (urinary incontinence).
Most pregnancy-related bladder leakage will go away within 3-6 months of delivery.
Why is bladder leakage so common for pregnant and postpartum people?
Growing babies take up room
As babies grow, they put pressure on your bladder, urethra and pelvic floor muscles.
Changing hormones weaken your muscles
During pregnancy, some of the hormones that prepare your body for delivery make it harder to hold in pee because they cause:
- Weakened pelvic floor muscles
- Increased elasticity of tendons & ligaments
- Increased muscle flexibility
Childbirth can damage the pelvic floor
Labor and delivery can cause postpartum bladder leakage by:
- Damaging pelvic nerves or the pelvic floor
- Damaging the urethra
- Causing your pelvic organs to drop (pelvic organ prolapse)
Pelvic floor damage is more common when:
- There’s a long or difficult delivery
- The baby is larger than 9 lbs.
- You have to push for a long time
- You have a deep tear to the perineum
- Forceps are used
Vaginal deliveries are more likely to lead to bladder leakage than C-sections. However, C-sections are major surgeries and have other risks.
Take back control of your bladder
If you have bladder leakage, there are several ways you can manage your symptoms.
- Wear bladder leakage pads or underwear, like Poise, Depend and Thinx for All Leaks, to help protect your clothing.
- See a pelvic floor therapist to help strengthen your pelvic muscles.
- Try to maintain a healthy body weight during and after pregnancy to relieve pressure on your bladder.
- Avoid foods that irritate your bladder, such as:
- Caffeine
- Citrusy and acidic foods
- Spicy foods
- Soda
- Eat high-fiber foods, like:
- Beans
- Berries
- Whole grains
Eating enough fiber helps you avoid straining when pooping. Straining can put extra pressure on your bladder.
- Keep a bladder journal and note the times of day and activities that make you leak. Using what you learn, try to go to the bathroom before those times.
- If you have overactive bladder, practice bladder training by peeing at regular times and slowly increasing the amount of time between peeing.
- In some cases, you may need surgery to repair the damaged muscles.
Sooner Is Better
Bladder leakage during and after pregnancy is common — but you don’t have to live with it forever. The sooner you start treatment, the better your results will be.
This educational resource was sponsored by Poise, a brand of Kimberly-Clark. Other Kimberly-Clark brands include Depend and Thinx for All Leaks.
Poise and Depend are registered trademarks of Kimberly-Clark. Thinx for All Leaks is a trademark of Kimberly-Clark.
- After Years of Living with Postpartum Bladder Leakage, I Was Able to Successfully Treat It ›
- After a Traumatic Vaginal Birth Two Years Ago, I Live with Bladder Leakage ›
- How to Know if You Have Urinary Incontinence ›
- How to Not Let Light Bladder Leakage Hold You Back ›
- Living With Incontinence, Without Shame ›
- What You Need to Know About Urinary Incontinence ›