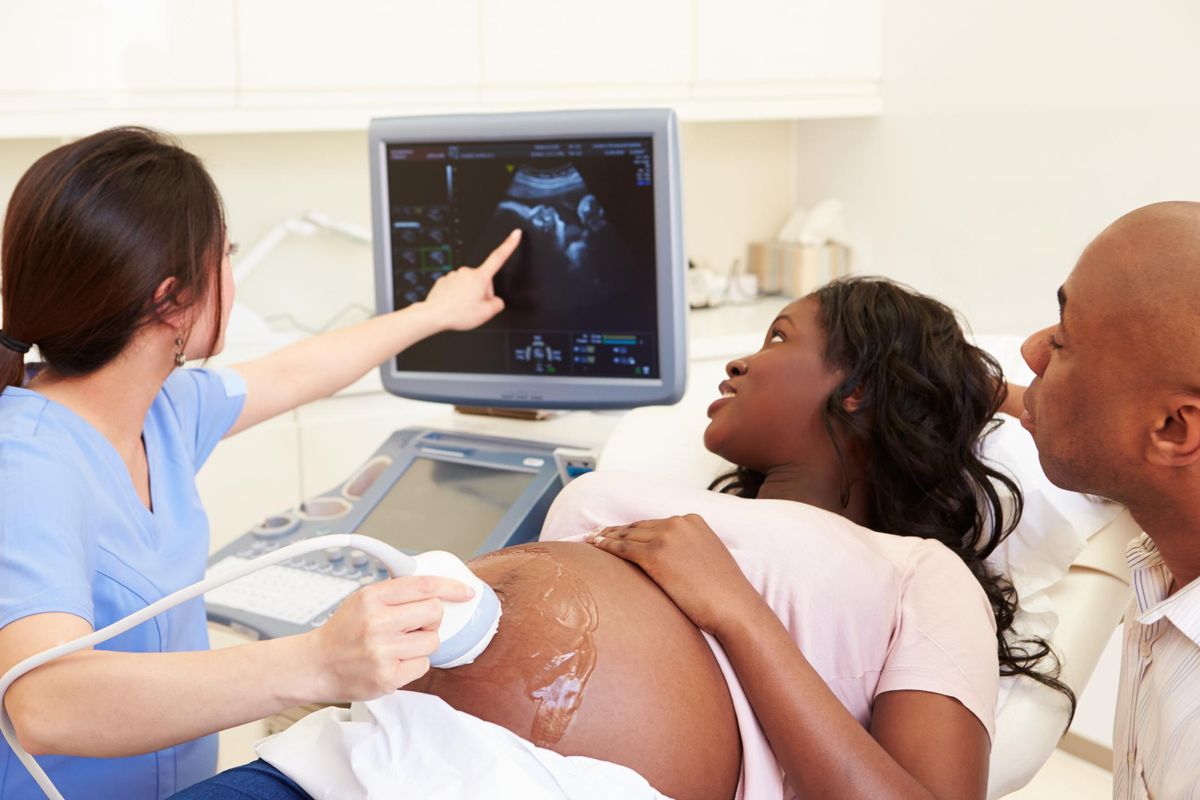
Near the end of your first trimester and early in the second trimester, your health care professional will talk with you about a variety of prenatal tests to assess the health of the fetus. It's up to you which ones you have done. For instance, if you have no intention of terminating the pregnancy if the tests do find a problem, you may want to skip them. However, even then, you may want to have the test so you can prepare yourself emotionally for the possibility of having a special-needs child.
The most common prenatal tests and the timing are outlined in the chart below.
| Test | What is it? | When/Where? |
| Genetic screening | If you have a family history of inherited diseases such as Tay-Sachs or thalassemia, consider genetic counseling to assess your risk of having a child with the disease. It is standard to offer all couples screening for cystic fibrosis. Certain ethnicities may predispose you to carrying genetic disorders. | Ideally, should be performed before conception, but may be done early in the pregnancy. The screening begins with a session with a genetic counselor and may involve some blood tests. |
| Chorionic villus sampling ( CVS ) | Placental cells are removed and tested for chromosomal and genetic disorders. | 10 to 12 weeks. Performed as an in-office procedure. |
| Fetal nuchal translucency | Uses ultrasound to assess the fold in the back of the fetus's neck to determine the risk of Down syndrome. | 10 to 14 weeks. Performed as an in-office procedure. |
| Amniocentesis | A needle is inserted into the amniotic sac and a bit of the amniotic fluid removed and examined. This test can provide information on various chromosomal and genetic abnormalities, including Down syndrome and neural tube defects. | After 15 weeks. Performed as an in-office procedure. |
| Ultrasound | Sound waves are used to help identify gestational age, detect multiple pregnancies, and identify any structural anomalies. | 18 to 20 weeks. Typically performed in the office or in a diagnostic center. |
| Serum marker screening | Blood test used to screen for neural tube defects and trisomies 21 and 18. | 16 to 18 weeks. Performed in the office. |