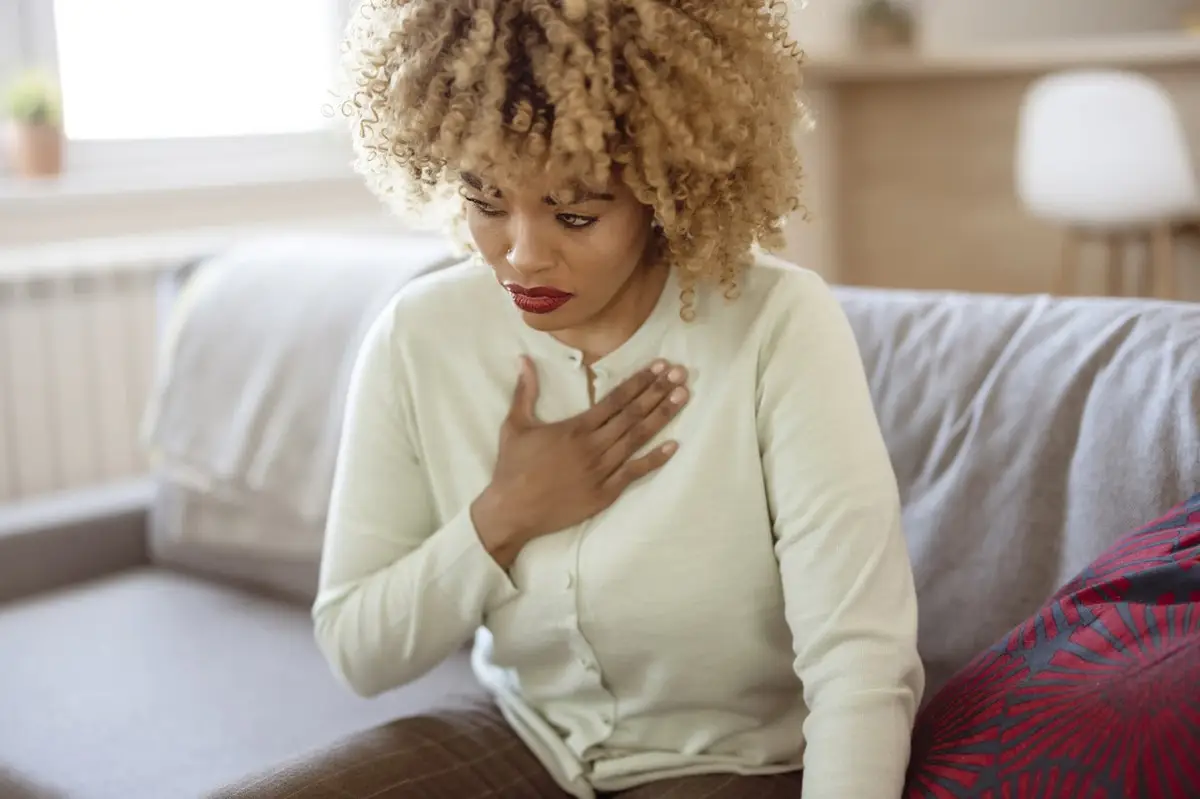
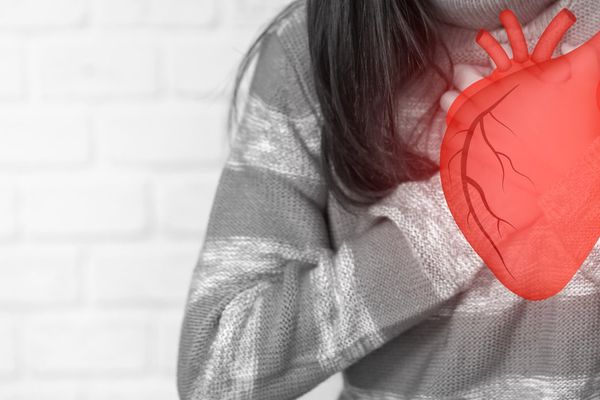
Heart disease is the number one cause of death for women and people assigned female at birth in the United States. That means you may be at risk for serious heart problems, such as heart attack or cardiac arrest.
You’ve probably heard of both these life-threatening conditions, but they’re not the same.
Here’s what you need to know about symptoms and treatment for a heart attack vs. cardiac arrest.
What’s the difference between a heart attack and cardiac arrest?
During cardiac arrest, the heart stops beating. During a heart attack, the heart is still beating.
A heart attack is caused by blockage (“circulation problem”) and cardiac arrest is caused by abnormal heart rhythm (“electrical problem”).
- A heart attack happens when the blood flow to your heart is blocked and your heart doesn’t have oxygen to work properly.
- Cardiac arrest happens when your heart suddenly stops beating and pumping blood to the rest of the body. This is caused by abnormal heart rhythm in the heart’s lower chambers and can be fatal within minutes without medical attention.
What are the symptoms of a heart attack in women?
Symptoms of heart attacks are different in women than in men. The most common symptom for both is chest pain — but women often have symptoms you don’t immediately think of.
Other symptoms include:
- Extreme fatigue
- Shortness of breath
- Pain and/or discomfort in the neck or jaw
- Pain and/or discomfort in one or both arms
- Back pain in the upper back or abdomen
- Lightheadedness
- Nausea
- Sweating
Symptoms of a heart attack can be mild or severe. You can also have no symptoms and still have a heart attack.
What are the symptoms of cardiac arrest in women?
Sudden cardiac arrest is a lot like it sounds — a life-threatening heart event that happens without warning.
But you can also have signs and symptoms of cardiac arrest. These can include:
- Loss of consciousness
- Dizziness
- Lightheadedness
- Heart palpitations
- Shortness of breath
- Vomiting or nausea
- Chest pain
A common symptom of cardiac arrest is loss of consciousness because the heart is no longer pumping blood to the rest of the body. So if you see someone drop to the ground, it may be cardiac arrest.
If you think someone is in cardiac arrest, call 911 and start cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) immediately. If a defibrillator is around, use it as soon as possible to shock the heart back into rhythm, and let the emergency medical providers know they may need one.
Read: Bystander CPR Saved My Husband’s Life >>
Time is key. Someone in cardiac arrest can die within minutes without CPR and medical attention.
What to do if you or someone else is having a heart attack
If you or someone around you is having symptoms of a heart attack, call 911 immediately. Every minute that goes by can be fatal and add damage to your heart.
Heart attacks are a risk factor for cardiac arrest, but most heart attacks don’t immediately lead to cardiac arrest. Talk to your healthcare provider about your risk for heart disease and what you can do to reduce your risk for heart attacks and cardiac arrest.
- What Is a Heart-Healthy Diet? ›
- I Never Felt Chest Pain, but I Had a Heart Attack ›
- How Women's Heart Attack Symptoms Are Different Than Men's ›
- Fast Facts: What Women Need to Know About Cardiovascular Disease ›
- Heart Disease ›
- Stroke vs. Heart Attack: Know the Signs & Symptoms ›
- Symptoms of Heart Attacks in Women ›
- What Is Heart Disease? - HealthyWomen ›
- Causes of Chest Pain That Aren't a Heart Attack - HealthyWomen ›